News Release
Gross Domestic Product (Third Estimate), GDP by Industry, and Corporate Profits (Revised), 1st Quarter 2021
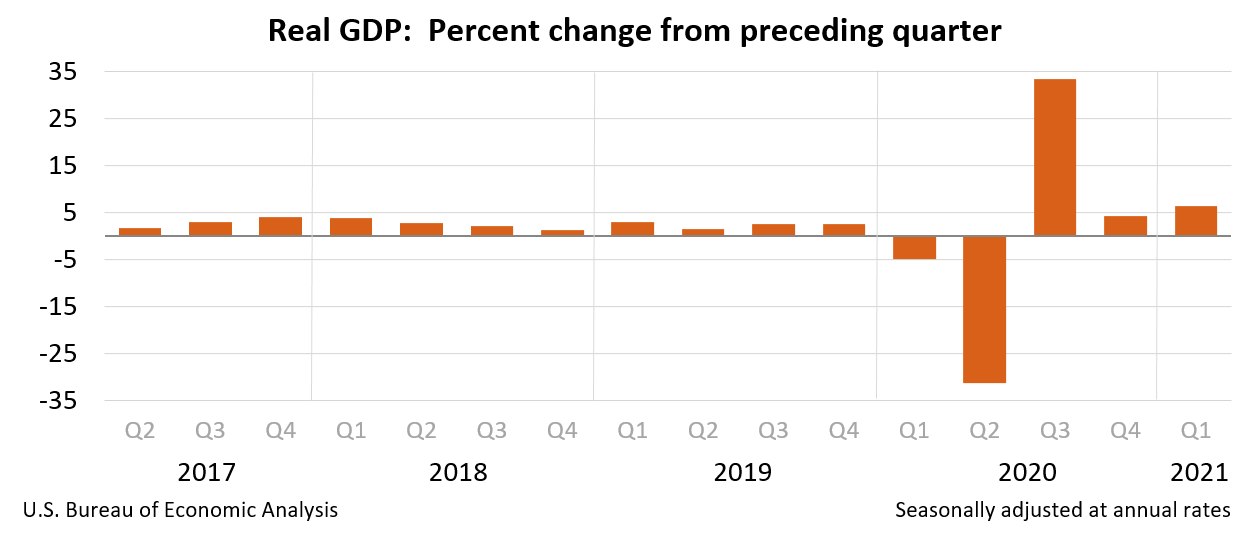
Real gross domestic product (GDP) increased at an annual rate of 6.4 percent in the first quarter of 2021 (table 1), according to the "third" estimate released by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. In the fourth quarter, real GDP increased 4.3 percent.
The “third” estimate of GDP released today is based on more complete source data than were available for the "second" estimate issued last month. In the second estimate, the increase in real GDP was also 6.4 percent. Upward revisions to nonresidential fixed investment, private inventory investment, and exports were offset by an upward revision to imports, which are a subtraction in the calculation of GDP (see "Updates to GDP").
The increase in real GDP in the first quarter reflected increases in personal consumption expenditures (PCE), nonresidential fixed investment, federal government spending, residential fixed investment, and state and local government spending that were partly offset by decreases in private inventory investment and exports. Imports increased (table 2).
The increase in PCE reflected increases in durable goods (led by motor vehicles and parts), nondurable goods (led by food and beverages), and services (led by food services and accommodations). The increase in nonresidential fixed investment reflected increases in equipment (led by information processing equipment) and intellectual property products (led by software). The increase in federal government spending primarily reflected an increase in payments made to banks for processing and administering the Paycheck Protection Program loan applications as well as purchases of COVID-19 vaccines for distribution to the public. The decrease in private inventory investment primarily reflected a decrease in retail trade inventories (mainly by motor vehicles and parts dealers).
Current dollar GDP increased 11.0 percent at an annual rate, or $566.8 billion, in the first quarter to a level of $22.06 trillion. In the fourth quarter, GDP increased 6.3 percent, or $324.4 billion (table 1 and table 3). More information on the source data that underlie the estimates is available in the Key Source Data and Assumptions file on BEA’s website.
The price index for gross domestic purchases increased 4.0 percent in the first quarter, compared with an increase of 1.7 percent in the fourth quarter (table 4). The PCE price index increased 3.7 percent, compared with an increase of 1.5 percent. Excluding food and energy prices, the PCE price index increased 2.5 percent, compared with an increase of 1.3 percent.
Gross Domestic Income and Corporate Profits
Real gross domestic income (GDI) increased 7.6 percent in the first quarter, compared with an increase of 19.4 percent in the fourth quarter. The average of real GDP and real GDI, a supplemental measure of U.S. economic activity that equally weights GDP and GDI, increased 7.0 percent in the first quarter, compared with an increase of 11.6 percent in the fourth quarter (table 1).
Profits from current production (corporate profits with inventory valuation and capital consumption adjustments) increased $55.2 billion in the first quarter, in contrast to a decrease of $31.4 billion in the fourth quarter (table 10).
Profits of domestic financial corporations decreased $6.4 billion in the first quarter, in contrast to an increase of $17.5 billion in the fourth quarter. Profits of domestic nonfinancial corporations increased $72.1 billion, in contrast to a decrease of $48.2 billion. Rest-of-the-world profits decreased $10.6 billion, compared with a decrease of $0.7 billion. In the first quarter, receipts increased $34.2 billion, and payments increased $44.8 billion.
Updates to GDP
In the third estimate, the change in first-quarter real GDP was the same as in the second estimate. Upward revisions to nonresidential fixed investment, private inventory investment, exports, and PCE were offset by an upward revision to imports. For more information, see the Technical Note. For information on updates to GDP, see the "Additional Information" section that follows.
| Advance Estimate | Second Estimate | Third Estimate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Percent change from preceding quarter) | |||
| Real GDP | 6.4 | 6.4 | 6.4 |
| Current-dollar GDP | 10.7 | 11.0 | 11.0 |
| Real GDI | … | 6.8 | 7.6 |
| Average of Real GDP and Real GDI | … | 6.6 | 7.0 |
| Gross domestic purchases price index | 3.8 | 3.9 | 4.0 |
| PCE price index | 3.5 | 3.7 | 3.7 |
| PCE price index excluding food and energy | 2.3 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
Real GDP by Industry
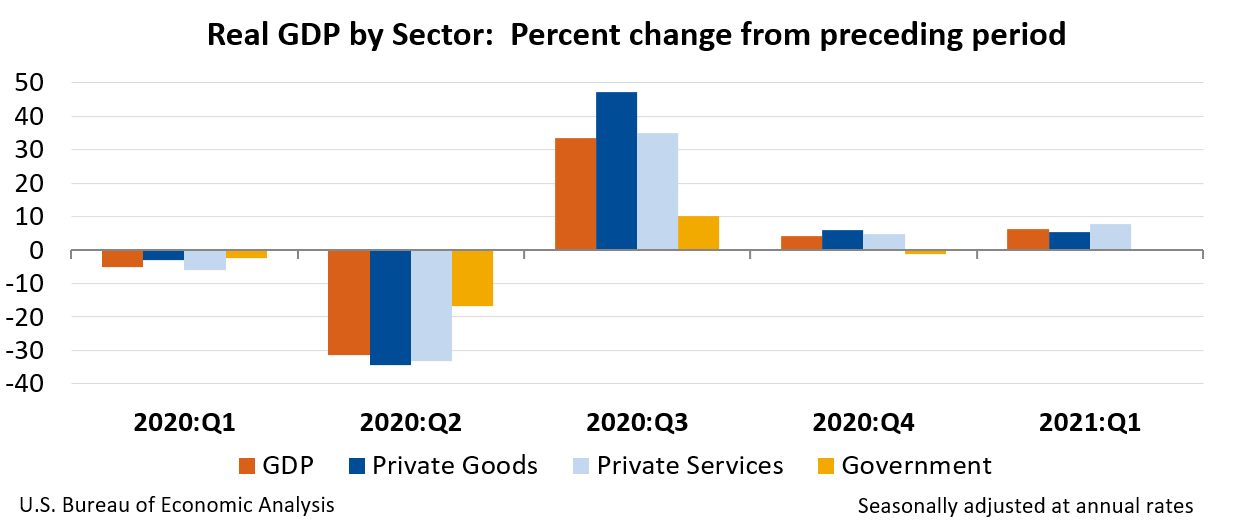
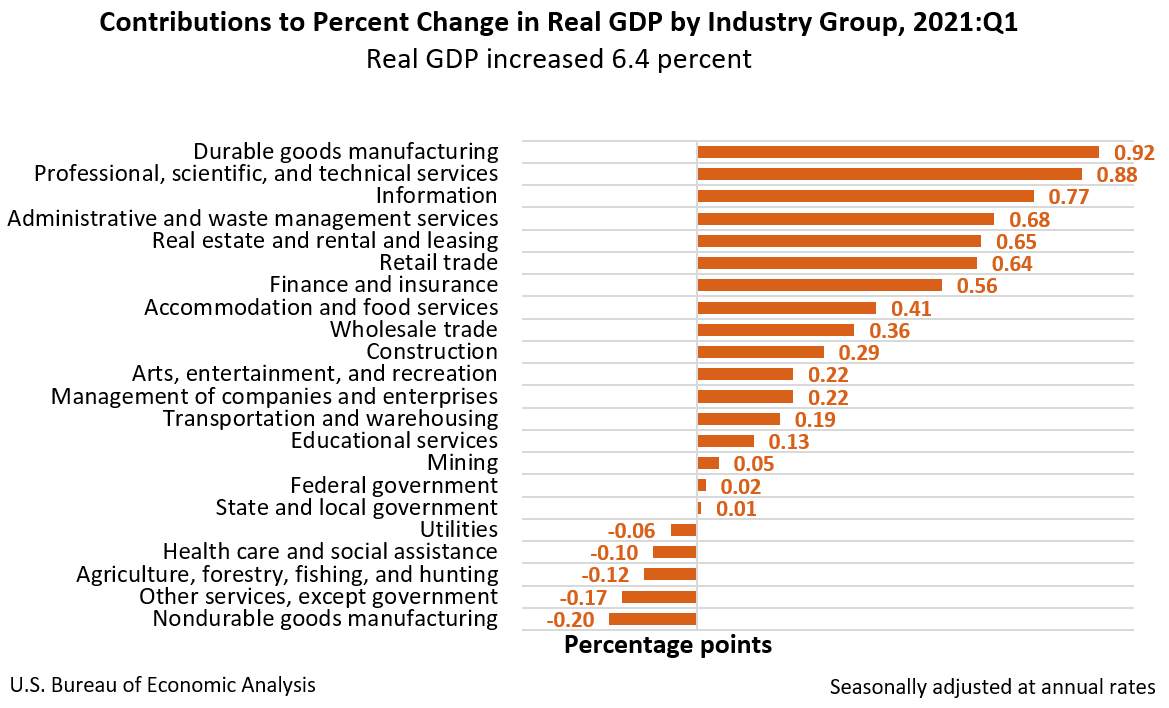
Today’s release includes estimates of GDP by industry, or value added—a measure of an industry’s contribution to GDP. In the first quarter, private goods-producing industries increased 5.4 percent, private services-producing industries increased 7.7 percent, and government increased 0.2 percent (table 12). Overall, 17 of 22 industry groups contributed to the first-quarter increase in real GDP.
The increase in private goods-producing industries primarily reflected an increase in durable goods manufacturing (led by computer and electronic products, fabricated metal products, and machinery). The increase was partly offset by decreases in nondurable goods manufacturing (led by petroleum and coal products) and agriculture, forestry, fishing, and hunting (led by farms).
The increase in private services-producing industries primarily reflected increases in professional, scientific, and technical services; information (led by data processing, internet publishing, and other information services); administrative and waste management services (led by administrative and support services); real estate and rental and leasing; and retail trade. These increases were partly offset by decreases in other services (which includes activities of political organizations); healthcare and social assistance (led by ambulatory health care services); and utilities.
The increase in government reflected increases in federal as well as state and local.
Gross Output by Industry
Real gross output—principally a measure of an industry’s sales or receipts, which includes sales to final users in the economy (GDP) and sales to other industries (intermediate inputs)—increased 8.9 percent in the first quarter (table 16). Private goods-producing industries decreased 1.7 percent, private services-producing industries increased 13.4 percent, and government increased 6.0 percent. Overall, 17 of 22 industry groups contributed to the increase in real gross output, led by retail trade, finance and insurance, and information. A decrease in nondurable goods manufacturing was the most notable offset to these increases.
* * *
Next release, July 29, 2021 at 8:30 A.M. EDT
Gross Domestic Product, Second Quarter 2021 (Advance Estimate) and Annual Update
* * *